-40%
antique Tichelaar Makkum Holland charger, delft polychrome plate dish 35,7cm 14"
$ 205.92
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
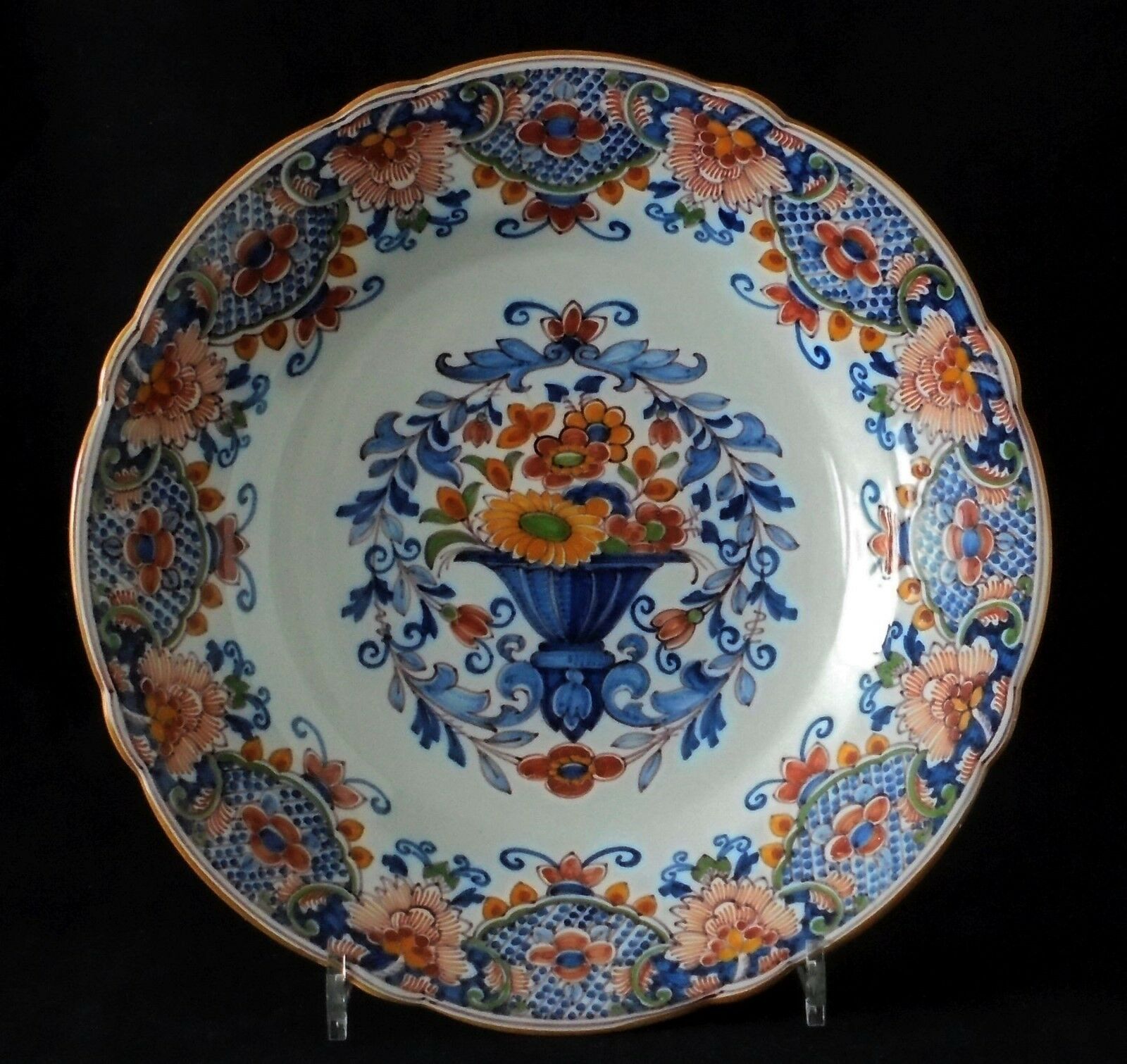
code: TM-AFa large, decorative Dutch delftware charger - plate - dish,
with the possibility to hang on the wall
fully handpainted, beautiful polychrome decoration,
made by
Tichelaar Makkum
in Friesland, the Netherlands, Holland
with a floral border design and in the center a bouquet in a vase
marked in manganese underglaze with the Makkum Tichelaar mark, and 967, and H.K
condition:
firm, clean & clear, no scratches to the decor, no restoration, 2 small glaze chips - too small to catch on picture and only visible on the side, at the backside of the rim you can see 2 spots - these are not chips but paint spots under the glaze (spots are pointed out in red)
age: it is impossible for us to date this plate, but certainly after 1895
diameter: 35,7 cm / circa 14.06 inch
weight: circa 1128 gr.
-
please see our other items
for more Makkum Tichelaar, Delftware and Porceleyne Fles / Royal Delft items -
for more info on Tichelaar Makkum see more below
world wide shipping:
- you will be ordering registrated shipment provided by PostNL from The Netherlands, EU
- this will be according to the PostNL conditions
- if possible with tracking, priority and
insurance offered by PostNL for loss during shipment
- the shippingcosts differ per country
- combined shippingcosts by weightcategory: 0-2 / 2-5 / 5-10 kg
we are: delta 98 den haag
The Hague, The Netherlands, EU
registrated at
Chambers of Commerce in The Netherlands / KvK Haaglanden: file 27133335
ceramics from Makkum
Tichelaar is a Dutch pottery
company, now called:
Royal Tichelaar Makkum / Koninklijke Tichelaar
Makkum,
was established in 1572 in Makkum, a village situated on the banks of the IJsselmeer / Lake IJssel, a lake since 1932, but before it was sea: the Zuiderzee / Southern Sea, in the northern Dutch province Friesland of The Netherlands
.
After initially producing bricks
and later pottery and tiles
, the company has focused on traditional decorative pottery since 1890. As the company in Makkum has always made ceramics, Tichelaar Makkum is regarded as one of the oldest companies in the Netherlands
.
History:
In 1960, the company received the designation
Koninklijk
(Royal), on the occasion of its 300th anniversary. Later research showed that the company had been active even earlier and it celebrated its 400th anniversary in 1994, on the basis of the results of historical research. In 2007, documentation was discovered showing that the company was already active in 1572, as a Spanish
map of that date shows bricaría (Spanish for brickworks
) in Makkum. In 1689, Freerk Jans a brickmaker, so called tichelaar, bought one half of the works, and then in 1694, the other half. During the eighteenth and nineteenth century, it was mainly dishes for daily use and tiles
that were made in the clay ovens. Around 1865, the demand for dishes decreased. The brothers Jelmer and Jan started a drastic innovation process, whereby the company could continue as a factory for decorative pottery. Throughout the ages, the company has retained the old working methods, working with locally dug clay that is covered in a white tin
glaze after the first firing, called the Majolica technique
. In 1882, the use of plaster moulds was introduced, increasing the assortment of decorative pottery.
Materials and processes:
The raw material is yellow or red firing sea clay
that is abundant in the west of the province of Friesland
. Tichelaar bought German
clay but also dug his own clay from the neighbouring countryside, leading to the local word 'afgeticheld' to describe a meadow that had been dug up. The clay was mixed with marl
in the pottery washing plant and then stored in a cellar to keep it frost-free. Shortly before processing, the clay was thoroughly kneaded and mixed again and then cut to size or punched. After drying, it was baked to biscuit, called raw material, which was then covered in white on the front. On the back, the dishes got a layer of [lead] glaze. After the artists had applied their decoration to the lead glaze, they were fired a second time. Two sorts of glaze were used; one transparent and one usually white covering glaze, called lead glaze and white glaze respectively, which were both prepared in the company. For the decoration, coloured glazes were prepared in the company. They were ground to a fine powder and when mixed with water, they could be used for painting. There were five colours (blue, purple, green, yellow and orange), though in practice it was usually blue and purple that were used.